How to Compute Debt to Equity Ratio
How to Compute Debt to Equity Ratio
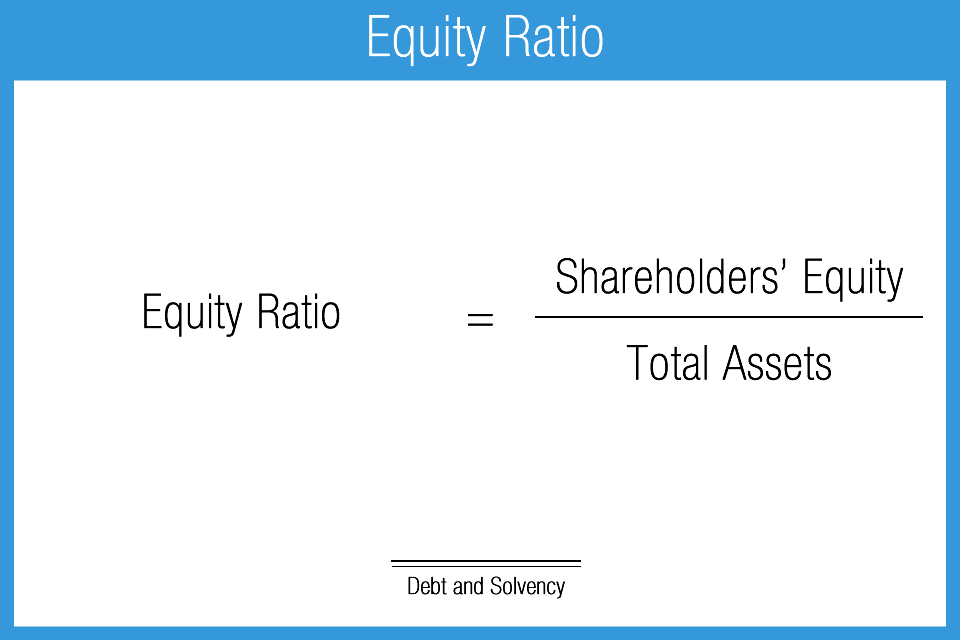
This formula provides a quick and straightforward way to assess a company’s financial leverage. The D/E Ratio is also crucial for comparing companies within the same industry. Different industries have different capital structures and financing norms, making it essential to compare a company’s debt-to-equity ratio against industry averages and benchmarks. This comparison provides valuable context, helping investors and analysts determine whether a company’s leverage is in line with industry standards or if it stands out as an outlier.
Debt to Equity Ratio Explained
The 10-K filing for Ethan Allen, in thousands, lists total liabilities as $312,572 and total shareholders’ equity as $407,323, which results in a D/E ratio of 0.76. Put another way, if a company was liquidated and all of its debts were paid off, the remaining cash would be the total shareholders’ equity. However, a low D/E ratio is not necessarily a positive sign, as the company could be relying too much on equity financing, which is costlier than debt. In general, if a company’s D/E ratio is too high, that signals that the company is at risk of financial distress (i.e. at risk of being unable to meet required debt obligations). Investors who want to take a more hands-on approach to investing, choosing individual stocks, may take a look at the debt-to-equity ratio to help determine whether a company is a risky bet. Debt-to-equity ratio is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to evaluating stocks.
Importance of the Debt to Equity Ratio
There also are many other metrics used in corporate accounting and financial analysis used as indicators of financial health that should be studied alongside the D/E ratio. Capital-intensive sectors, such as utilities and manufacturing, often have higher ratios due to the need for significant upfront investment. In contrast, industries like technology or services, which require less capital, tend to have lower D/E ratios.
How do companies improve their debt-to-equity ratio?
A company with a D/E ratio that exceeds its industry average might be unappealing to lenders or investors turned off by the risk. As well, companies with D/E ratios lower than their industry average might be seen as favorable to lenders and investors. Each industry has different debt to equity ratio benchmarks, as some industries tend to use more debt financing than others. A debt ratio of .5 means that there are half as many liabilities than there is equity.
✝ To check the rates and terms you may qualify for, SoFi conducts a soft credit pull that will not affect your credit score. It’s easy to get started when you open an investment account with SoFi Invest. You can invest in stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, alternative funds, and more. SoFi doesn’t charge commissions, but other fees apply (full fee disclosure here).
Why are D/E ratios so high in the banking sector?
We can see below that for Q1 2024, ending Dec. 30, 2023, Apple had total liabilities of $279 billion and total shareholders’ equity of $74 billion. Suppose a company carries $200 million in business software explained total debt and $100 million in shareholders’ equity per its balance sheet. Many companies borrow money to maintain business operations — making it a typical practice for many businesses.
- Specifically, preferred stock with dividend payment included as part of the stock agreement can cause the stock to take on some characteristics of debt, since the company has to pay dividends in the future.
- As you can see, company A has a high D/E ratio, which implies an aggressive and risky funding style.
- Other definitions of debt to equity may not respect this accounting identity, and should be carefully compared.
- A debt due in the near term could have an outsized effect on the debt-to-equity ratio.
From the above, we can calculate our company’s current assets as $195m and total assets as $295m in the first year of the forecast – and on the other side, $120m in total debt in the same period. The formula for calculating the debt-to-equity ratio (D/E) is equal to the total debt divided by total shareholders equity. If preferred stock appears on the debt side of the equation, a company’s debt-to-equity ratio may look riskier.
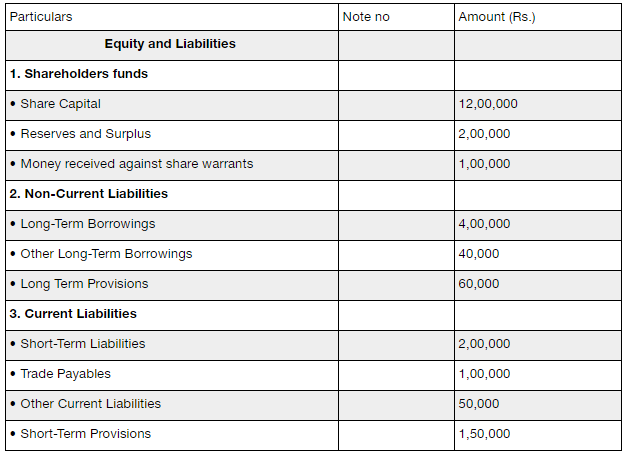
A higher debt to equity ratio indicates that more creditor financing (bank loans) is used than investor financing (shareholders). This number can tell you a lot about a company’s financial health and how it’s managing its money. Whether you’re an investor deciding where to put your money or a business owner trying to improve your operations, this number is crucial. This looks at the total liabilities of a company in comparison to its total assets.
